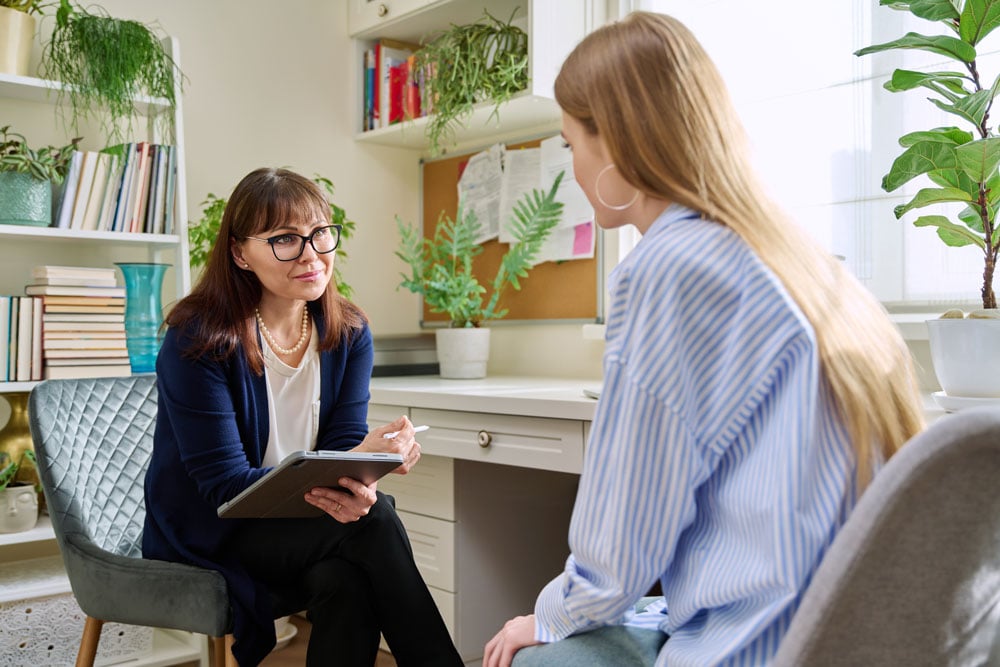
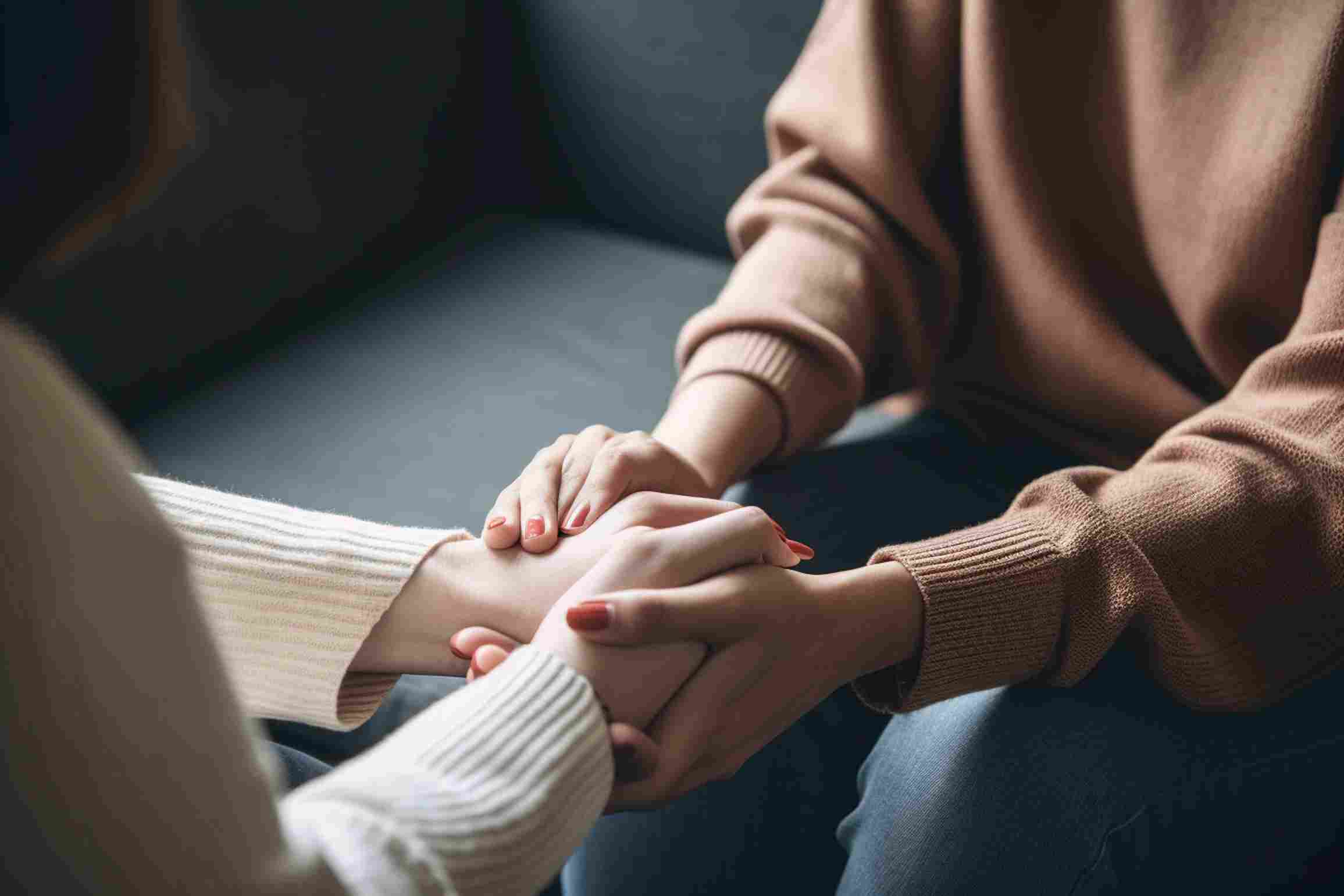
Comorbid bipolar disorder and substance abuse presents a treatment challenge for any SUD provider. The two conditions have a complex relationship, and the interplay between diagnoses differs for every patient. Effective treatment requires SUD clinics to consider these...
Dual diagnosis treatment is among the most demanding challenges facing substance use disorder (SUD) clinics. Data suggests that more than 15% of individuals with SUD also have a serious mental illness (SMI) and nearly 30% of individuals with SMI also have SUD, yet only 10% of...
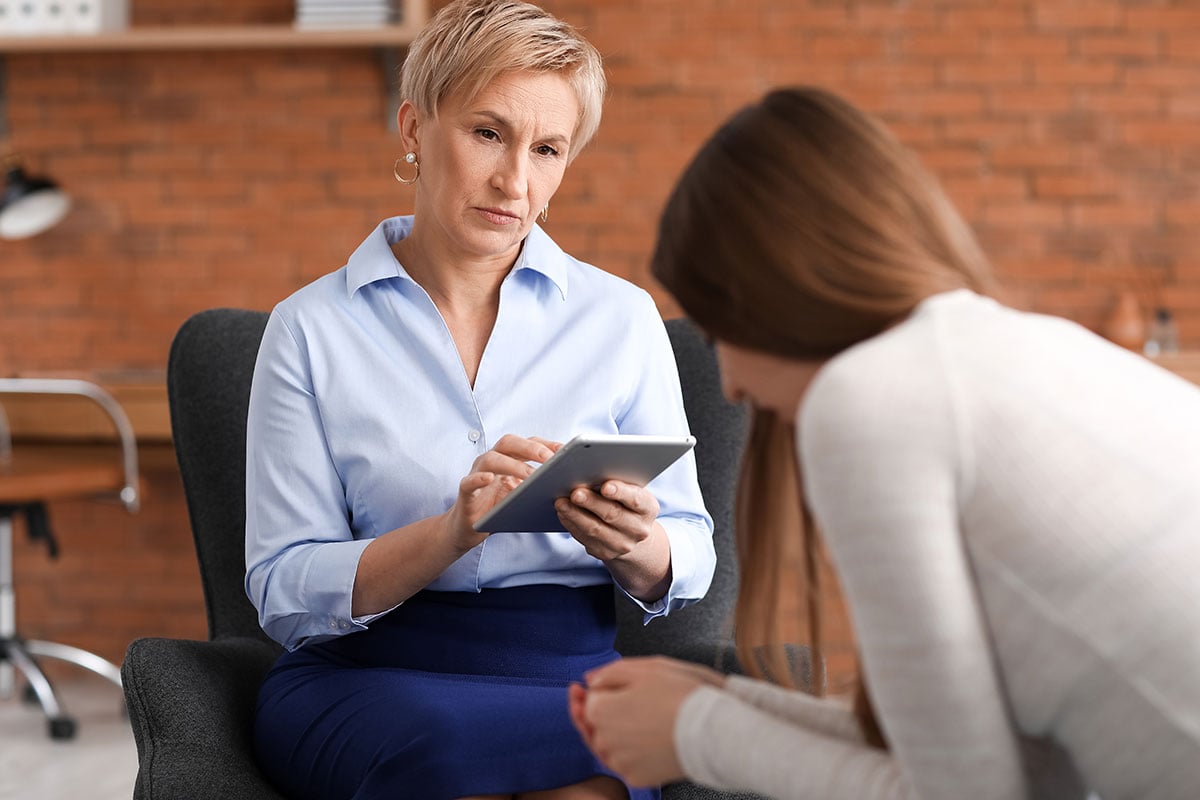
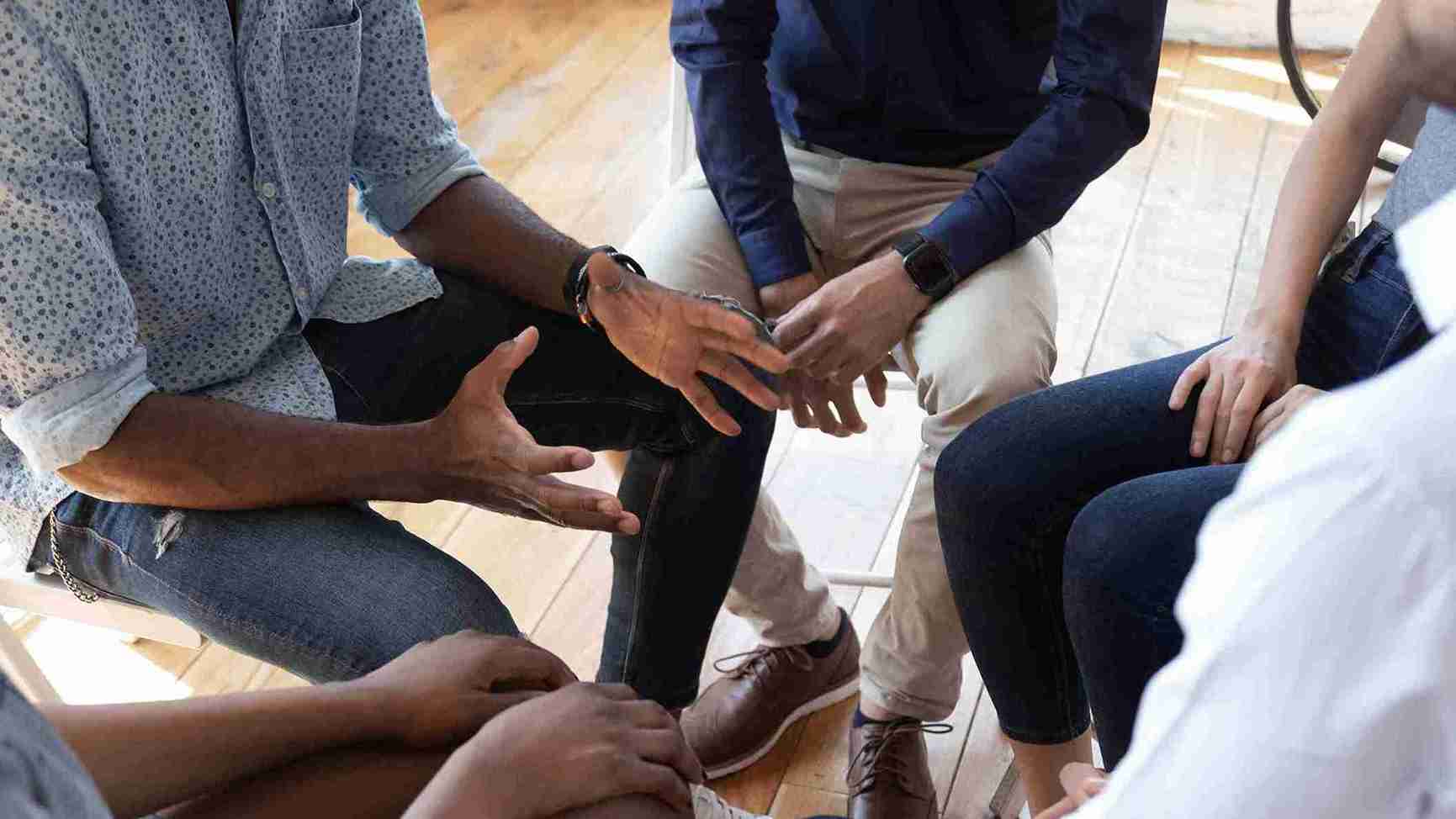
A carefully planned substance use disorder (SUD) assessment is essential to the treatment process. Unless the clinical team understands how addiction affects the patient and whether any other co-occurring disorders are at play, developing an effective treatment plan is...
Men's Health Awareness Month in November provides a unique opportunity to explore the intricate connection between mental and physical well-being. This month serves as a reminder of the complex interplay between these two aspects and the critical need for early intervention and...
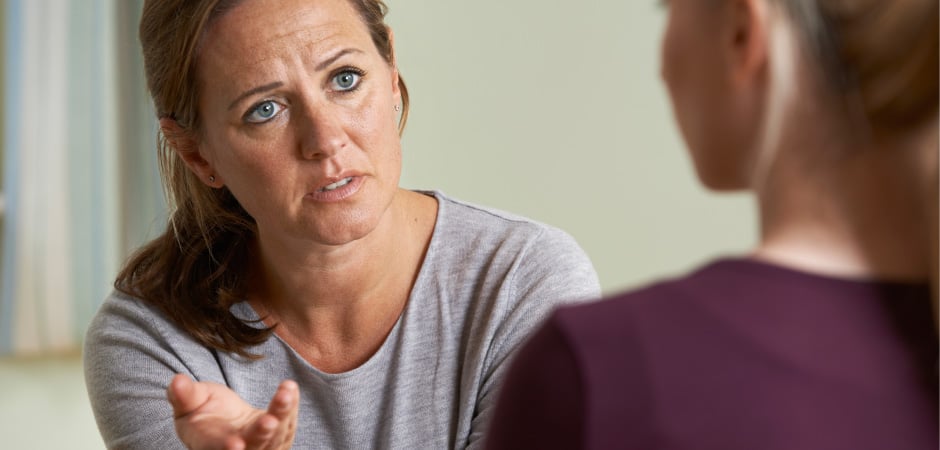
Anxiety and substance use disorder (SUD) are among the most common psychiatric diagnoses in the United States, with a respective lifetime prevalence of 28.8% and 14.6%. Psychiatric Times has noted that in any 12 months, 33% to 45% of individuals with anxiety disorder will ...
The most recentNational Survey of Drug Use and Health showed that approximately18 million adults aged 18 or older in 2021 had a co-occurring mental illness and illicit drug or alcohol use disorder in the prior year.
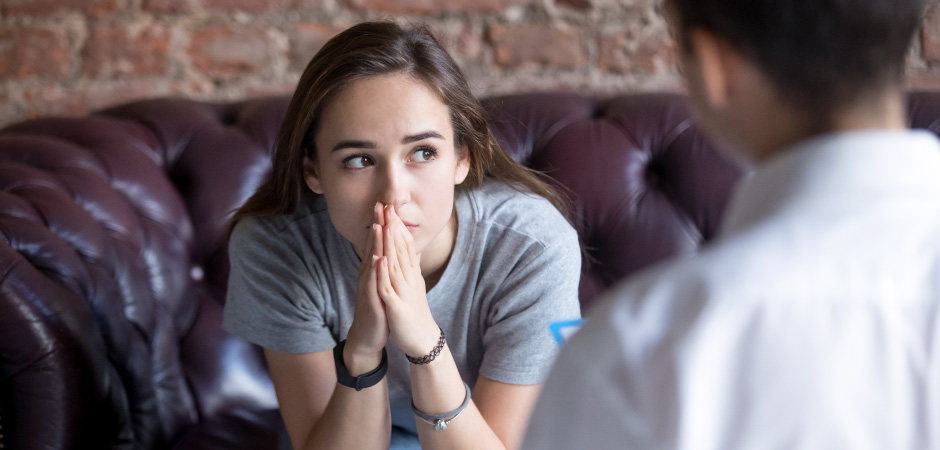
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), approximately half of people with a mental illness will develop a co-occurring substance use disorder (SUD) in their lifetimes and vice versa. One of the most common co-occurring combinations isdepression and substance use




.png)


%20(6)-1.jpg)


.jpeg)